Examples of the Victorian Gothic Architectural Style in College Chapels

Historical Significance
When you think of Medieval times, knights and castles might first come to mind while in fact this period spans all the way from the Romans to the Renaissance. For over 600 years, civilization underwent cultural and religious change. Architecture has had a strong cultural influence, bringing about massive cathedrals and impressive public works. Gothic Architecture in particular had its effect on civilization and markers of its importance are still apparent today. The Gothic style was introduced towards the beginning of the 12th century. Its appearance in the latter half of the Middle Ages came in the form of church design. Many European Churches were fashioned in Gothic style to create a feeling of worldly-transcendence. As the Middle Ages gave way to an enlightenment period, the Gothic style turned into the Renaissance. Gothic influence was not to re-surface for 700 years until a prominent style came into significance towards the 19th century. The revival of Gothic Architecture, now known as High Victorian Gothic, took a refined and advanced look into the imposing style of its genus. High Victorian Gothic Architecture originated in England. Often used for more substantial buildings such as churches or government offices, this style can be associated with a higher stature of importance. Many college chapels revisited the Gothic style and are testaments to the beauty of this era. Examples of High Victorian elements found in college churches throughout the United States is numerous, but there are specific buildings which especially amplify this style’s influence on modern Architecture.
Common Features of High Victorian Gothic Architecture
- Barrel Vault
- Ribbed Vault
- Groin Vault (Groining)
- Lancet (Lancet Window)
- Pointed Arches
- Cross-Shaped Floor Plan
- Stained Glass Windows
A staple in Gothic style and the gothic revival which we call High Victorian is the design of the ribbed vault. Similar to the barrel vault, the ribbed vault is a continuous roof of arches. The ribbed vault is a conglomerate of arches which have an inner beam cross sectioning the hall.


Canning recently finished gilding and faux finishing Christ’s Chapel at Hillsdale College. This Church has a clear barrel vault connecting to the pillars on either side.
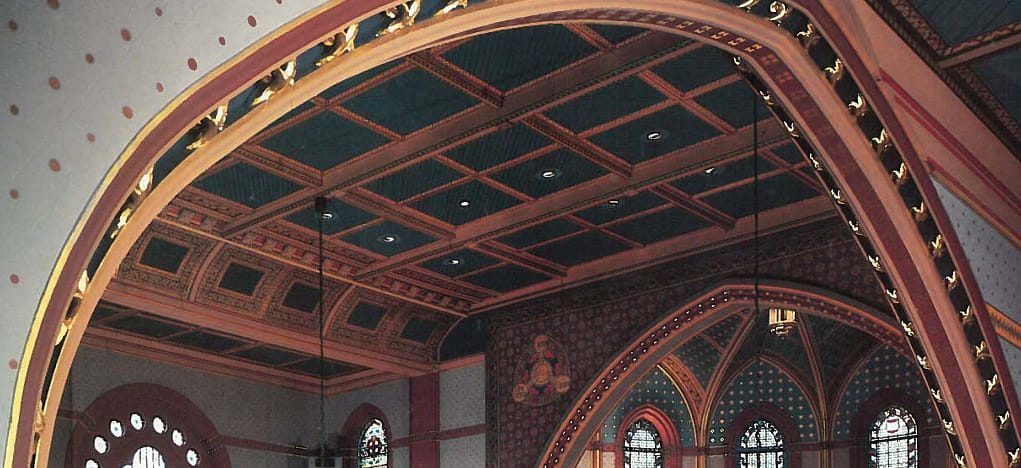
Princeton University Chapel


The vault in the picture above has multiple ribs connecting to the roof. Stemming from the pillars connected to the wall, these ribs glide up the ceiling and connect with one another in a pattern. In the particular case of Princeton University’s Chapel, the pillars on the wall are divided by long, narrow stained-glass windows. These windows are another feature made popular in Gothic style. stud to amplify their importance in the design. You can also see a second High Victorian feature in this photo which makes up the ribbed vault. This is a pointed arch. Arch shapes have changed over different styles of architecture throughout the years. The Romans dominated the round arch while the pointed arch came into style towards the twelfth century (Gothic).


St. Mary’s Church in Norwalk restored by Canning is another example of groin vaults with pointed arches. The ribs connect to the top beam which runs down the center of the nave.
Duke University Chapel
The Chapel at Duke University has a series of arches similar to the previous churches but also conveys another feature of High Victorian architecture; the stained glass. Although it is not unique to Gothic style for there to be stained glass, the practice has been greatly influenced by the medieval artists. It is important to note that the glass is high above where the congregation would meet, letting light come in from above and illuminating the intricate carvings of the nave.
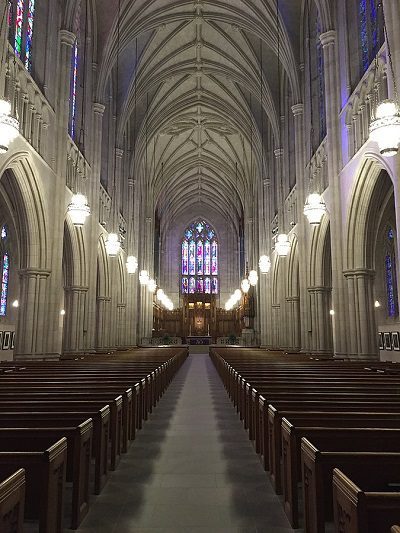


Duke’s chapel is not only High Victorian with its interior but the floor plan follows a common theme found in most gothic churches.
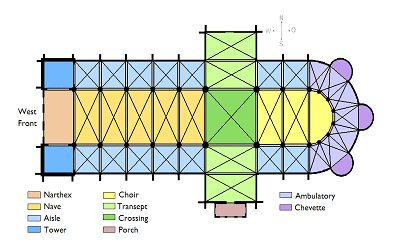

Common Cathedral plan.
This diagram shows the general blueprint of a common design for a High Victorian church. The chapel is designed to be in the shape of a cross, known as cruciform. The transepts, often containing side altars are on each side of the nave. The main alter can be found at the back end of the building in the apse. While not all Gothic churches have this type of structure, it is a common theme to be looked for in this style of architecture.
In the future when you visit college chapels or public churches, the influence of High Victorian Gothic style may be evident. It has helped cultivate the ornate designs found throughout cathedrals and basilicas and has given a new importance to the stained-glass window. The pointed arches have become a staple in many European Churches both in and out of college campuses. The High Victorian presence has influenced many of modern-day churches, introducing a fresh thought on a traditional idea.
